After coming to NC State, one of the clubs I was interested in joining with Engineers without Borders. Within EWB there are many international projects, including one called the Sierra Leon Renewable Energy Team. The goal of this team was to bring renewable energy to a place that lacks a stable source of energy. With Sierra Leon being split into the wet and dry season, solar panels were an efficient way to bring energy during the dry season. In completing such a project, one of the issues we faced was whether enough energy would be stored during the day to carry them through the night, and how the panels would be able to gather enough energy throughout the wet season. For this problem, UCLA created a product that uses radiative sky cooling to produce energy.
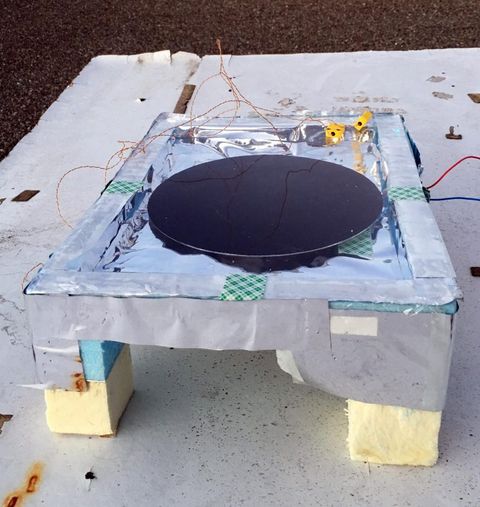
The concept of radiative cooling is the idea that the earth gives off heat waves that dissolve into cooler air as it rises into the atmosphere. As we know, the upper atmosphere is fairly frigid, which is thanks to this concept. Because this phenomenon occurs essentially anywhere there is a sky and somewhere the heat can be expelled from (the ground in most cases) scientists decided to attempt to harbor this energy to tackle the issue of electricity instability. The product that was developed captures some of this rising heat before it cools in the atmosphere, and converts it into useable energy. After testing it on a rooftop at night, the product was able to generate 25 milliwatts per square meter, and only cost $30 dollars to produce the actual device.
Scientists believe this item, which looks where similar to the falling sky from Chicken Little, could be a complementary product to solar panels, and generate electricity when solar panels otherwise could not. With the product being relatively cheap, this could be extremely helpful in impoverished societies, which subsequently have a lot of ground and sky space where this product could carry out its job. Currently, in Sierra Leon, the entire country is powered off a boat that is docked on the coast and extremely unstable which it comes to energy. If a product like this could be brought to countries like that, it could revolutionize the battle against climate change and modernized these underdeveloped societies.
Grossman, David. “Radiative Sky Cooling Could Be The Night Equivalent of Solar.” Popular Mechanics, Popular Mechanics, 16 Sept. 2019, https://www.popularmechanics.com/technology/infrastructure/a29036147/radiative-sky-cooling/.
